软件可测试性及常用Python测试技巧小结
问题
-
什么是代码的可测试性
-
如何写出可测试的代码?
-
有哪些常见的不好测试的代码?
写出可测试的代码
-
依赖注入
将对象的创建反转给上层逻辑,在外部创建好对象后再注入到下层代码中。
-
mock
若代码中依赖了外部系统或者不可控组件,比如,需要依赖数据库、网络通信、文件系统等,可以通过二次封装将被测代码与外部系统解依赖,提高可测试性.
比如用户类包含过期日期属性,假定我们需要对用户登录场景进行测试,其中一个判断逻辑是:如果用户过期,则返回登录失败。假如说_expire_data属性是经过封装的,未暴露对外接口进行修改,那么当测试过期用户登录时,可以对用户过期判定逻辑进行二次封装。
class User: id: int name: str _password: str _expire_date: datetime.datetime def is_expired()->bool: passdef user_is_expired(user: User): return user.is_expired()测试时可以对user_is_expired的返回值进行mock
def user_is_expired(user: User): return true
可能的问题
-
对外部服务的依赖
-
网络通信耗时
-
不可控因素
反模式
-
未决行为
代码输出是随机的,比如跟时间、随机数相关的代码。
-
滥用全局变量
-
滥用静态方法
-
复杂继承
-
高耦合代码
如何度量软件架构质量属性?
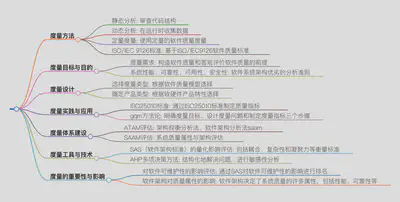
软件可测试性
软件测试的不同方面
-
功能
-
性能
常用的软件测试策略
- 模拟(mocking)
- 存根(stubbing)
单元测试
测试一段代码:
# solution.py
from algorithms.base import BaseSolution
from utils import timer
class Solution(BaseSolution):
@timer
def run(self, nums1: list, m: int, nums2: list, n: int) -> list:
nums1[m:] = nums2
nums1.sort()
return nums1
class Solution1(BaseSolution):
@timer
def run(self, nums1: list, m: int, nums2: list, n: int) -> list:
array = []
s1_index, s2_index = 0, 0
while s1_index<m or s2_index<n:
if s1_index == m:
array.append(nums2[s2_index])
s2_index += 1
elif s2_index == n:
array.append(nums1[s1_index])
s1_index += 1
elif nums1[s1_index]<nums2[s2_index]:
array.append(nums1[s1_index])
s1_index += 1
else:
array.append(nums2[s2_index])
s2_index += 1
return array
solutions = [
Solution,
Solution1
]
通过单元测试框架针对所测模块执行测试用例
# test.py
import unittest
from algorithms.leetcode.alg88 import solution, case
from copy import deepcopy
class MyTestCase(unittest.TestCase):
def test_algorithms(self):
_solution = solution.solutions
for solution_i in _solution:
print("===", solution_i.__name__)
for _case in case.cases:
case_copy = deepcopy(_case)
print(case_copy)
result = solution_i().run(*case_copy['input'])
print(result)
self.assertEqual(result, case_copy['output'])
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
单元测试中通过模拟高效避开耗时操作
通过unittest.mock下的patch和MagicMock对象模拟模块中的一些函数(可能耗时较长,但从测试流程上来说需要得到其返回值)。
示例:下面测试代码片段中test_02_generate_report方法的参数mock_prepare_data对forag.bussiness_rag.engine.ReportGeneratePipeline._prepare_data进行了模拟,模拟对象的返回值设置为self.information_table(实际测试时其可以直接读取固定的一个对象)。这样我们在测试generate_report这个方法时,可以固定且快速得到_prepare_data方法的结果,让我们更专注于测试给定数据下报告生成的效果。
import unittest
from unittest.mock import patch, MagicMock
@ddt
class TestBgeLargeEncoder(unittest.TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls):
cls.pipeline = ReportGeneratePipeline(article_gen_lm=article_gen_lm,
article_summary_lm=article_summary_lm,
article_style="bullet")
cls.outline_input = get_default_outline()
cls.information_table = NewsInformationTable(news_information,
encoder=SentenceTransformer(DEFAULT_ENCODING_MODEL))
cls.information_table.prepare_table_for_postprocess()
@data("人工智能", "AI", "神经网络")
def test_01_initialize(self, query):
result = TestBgeLargeEncoder.information_table.retrieve_information_plus([query])
print(f"Query {query}: got {[r.title for r in result]}")
self.assertIsInstance(result, list )
@patch('forag.bussiness_rag.engine.ReportGeneratePipeline._prepare_data')
def test_02_generate_report(self, mock_prepare_data: MagicMock):
mock_prepare_data.return_value = self.information_table
TestBgeLargeEncoder.pipeline._prepare_data = mock_prepare_data
article_response = TestBgeLargeEncoder.pipeline.generate_report(domain=domain,
outline=TestBgeLargeEncoder.outline_input,
news_data=news_data)
print(f"result: {article_response.code}, {article_response.msg}")
outputfile = f"{domain}-bullets-{TestBgeLargeEncoder.pipeline.article_gen_lm.model_type}-large-{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d-%H%M%S')}.md"
expected_code = FuncResponseCode.SUCCESS
self.assertEqual(article_response.code, expected_code, f"Expected {expected_code}, got {article_response.code}")
with open(outputfile, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(article_response.data)
self.assertTrue(os.path.exists(outputfile), f"File not found: {outputfile}")
# forag.bussiness_rag.engine.ReportGeneratePipeline
class ReportGeneratePipeline():
def generate_report(self, domain: str, outline: dict, news_data: list, filter_words=None) -> GeneralResponse:
"""
Parameters
----------
domain
outline
news_data
Returns
-------
"""
try:
information_table = self._prepare_data(news_data, filter_words)
except Exception as e:
logger.warning(repr(e))
return GeneralResponse(FuncResponseCode.ERROR, data=e, msg="数据加载失败,请稍后重试")
try:
article_with_outline = self._prepare_article(domain,
desctiption=outline.get("desc", ""),
sections=outline.get("sections", []))
report = self._generate_report(information_table, article_with_outline)
return GeneralResponse(code=FuncResponseCode.SUCCESS, data=report, msg="报告生成成功,请查看")
except Exception as e:
logger.warning(repr(e))
logger.error(traceback.format_exc())
return GeneralResponse(FuncResponseCode.ERROR, data=e, msg="报告生成异常,请稍后重试")

代码覆盖率
内联测试
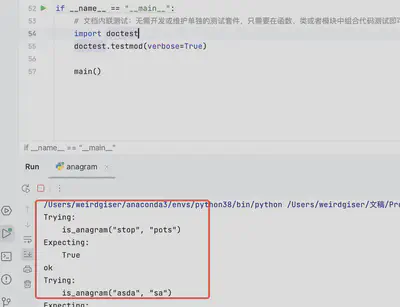
文档内联测试(doctest):无需开发或维护单独的测试套件,只需要在函数、类或者模块中组合代码测试即可。示例:
def is_anagram(word: str, other: str)->bool:
"""判断两个单词是否互为易位词
>>> is_anagram("stop", "pots")
True
>>> is_anagram("asda", "sa")
False
>>> is_anagram("stop", "otps")
True
"""
if len(word) != len(other):
return False
return sorted(list(word))==sorted(list(other))
测试自动化
-
数据驱动测试(DDT)
-
测试驱动开发(TDD)
测试报告生成
为了使测试结果更加直观和易于分析,通常会生成测试报告。有一些工具库能让我们快速产出一份测试报告。
相关框架或库
-
UnitTestReport
-
HTMLTestRunner
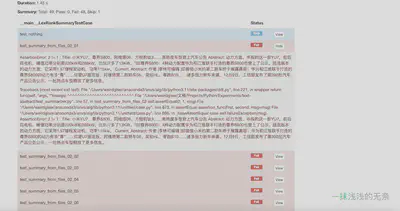
测试报告效果
- HTMLTestRunner
if __name__ == '__main__':
with open("reports/result.html", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
testrunner = HTMLTestRunner(verbosity=1,
report_name="摘要算法",
report_title="摘要算法测试结果",
descriptions=True,
stream=f,
combine_reports=False)
unittest.main(testRunner=testrunner, verbosity=1)
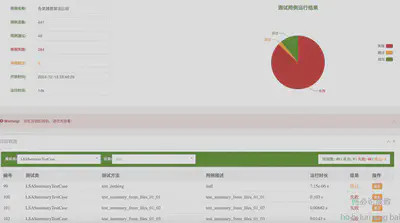
- BeautifulReport
if __name__ == '__main__':
test_suite = unittest.TestLoader().discover("test_summarizer")
result = BeautifulReport(test_suite)
result.report(filename='摘要算法测试报告-V2',
description='各类摘要算法比较',
report_dir='report', theme='theme_candy')

- ……
参考资料
-
《软件架构Python语言实现》-可测试性——编写可测试的代码(P58-P90)