「论文阅读」—GMAN: 一种用于交通预测的图多注意力网络
Abstract
Long-term traffic prediction is highly challenging due to the complexity of traffic systems and the constantly changing nature of many impacting factors. In this paper, we focus on the spatio-temporal factors, and propose a graph multi-attention network (GMAN) to predict traffic conditions for time steps ahead at different locations on a road network graph. GMAN adapts an encoder-decoder architecture, where both the encoder and the decoder consist of multiple spatio-temporal attention blocks to model the impact of the spatio-temporal factors on traffic conditions. The encoder encodes the input traffic features and the decoder predicts the output sequence. Between the encoder and the decoder, a transform attention layer is applied to convert the encoded traffic features to generate the sequence representations of future time steps as the input of the decoder. The transform attention mechanism models the direct relationships between historical and future time steps that helps to alleviate the error propagation problem among prediction time steps. Experimental results on two real-world traffic prediction tasks (i.e., traffic volume prediction and traffic speed prediction) demonstrate the superiority of GMAN. In particular, in the 1 hour ahead prediction, GMAN outperforms state-of-the-art methods by up to 4% improvement in MAE measure. The source code is available at this https URL.
文章
交通预测的目的是根据历史观测结果(如通过传感器记录的数据)预测道路网络中未来的交通状况(如交通量或速度)。它在许多现实世界的应用中发挥着重要作用。例如,准确的交通预测可以帮助交通机构更好地控制交通,以减少交通拥堵(Lv等,2018;Zheng等,2019)。
模型
细节
时空嵌入
交通状况的演化受基础道路网的限制(Lv等人,2018),有必要将道路网信息整合到预测模型。文章使用node2vec学习节点表示,将包含图结构信息的向量与整个模型共同训练。
空间注意力
建模道路间的空间相关性。关键思想是在不同时间步将不同的权重分配给不同顶点。
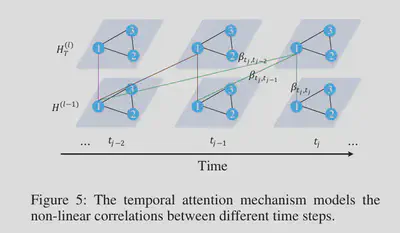
时间注意力
某一地点的交通状况与其历史观测值相关,且相关性随时间增长发送非线性变化。为了模拟这些特性,设计了一个时间注意机制来自适应地模拟不同时间步之间的非线性关系,如图所示。
注意力转换模块
在编码器和解码器之间,用于建模每一个未来时间步和历史时间步长的直接关系。
问题
- 很多交通流预测的文章都会将MAE指标交通流预测结果评价,而GMAN的文章中中直接以MAE作为损失函数,这像是一个trick。对于交通流预测而言,损失函数应该如何设计?